Big Data Security Insights | DataOps IT
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is one of the world’s most widely used cloud platforms, offering businesses the ability to build, scale, and manage applications securely and efficiently. One of AWS’s biggest strengths is its broad database portfolio. Unlike traditional database providers, AWS offers a purpose-built database approach — meaning it has different types of databases designed for different use cases.
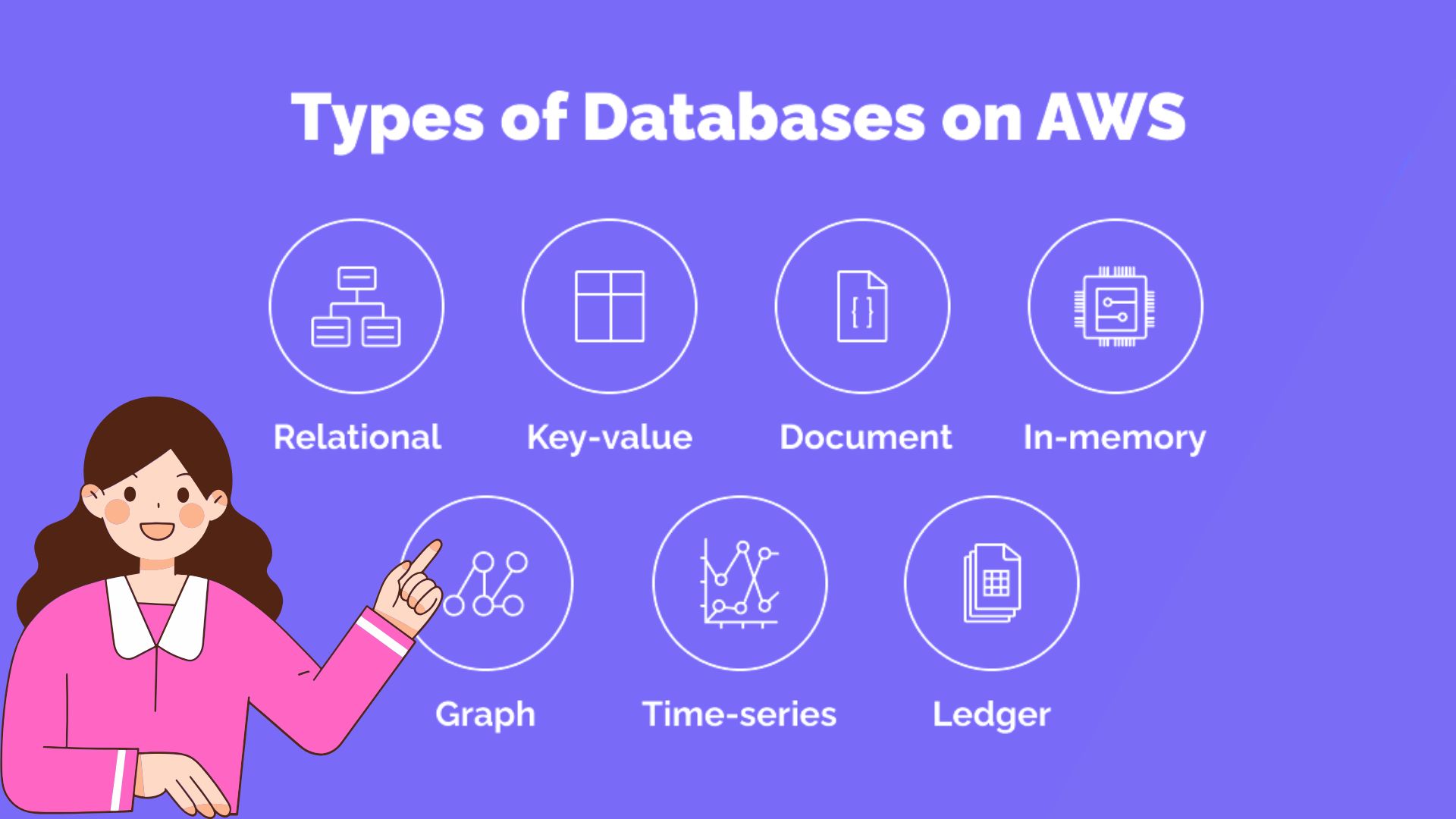
If you’re wondering how many types of databases AWS provides, the answer is over a dozen, broadly classified into categories such as relational, non-relational, in-memory, time series, graph, and ledger databases. Let’s explore them one by one.
1. Relational Databases (SQL-Based)
Relational databases are structured and work with SQL (Structured Query Language). They are ideal for applications that need complex queries and transactional integrity.
- Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service): Supports multiple engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle, and SQL Server.
- Amazon Aurora: A MySQL and PostgreSQL-compatible relational database built for high performance and scalability.
Use Case: E-commerce platforms, ERP systems, customer relationship management (CRM) applications.
2. Non-Relational (NoSQL) Databases
NoSQL databases are designed for flexibility and scale, handling unstructured or semi-structured data.
- Amazon DynamoDB: A fully managed key-value and document database with single-digit millisecond performance.
- Amazon DocumentDB (with MongoDB compatibility): A document database designed to work with JSON-like data.
Use Case: Mobile apps, IoT applications, content management systems, and real-time big data workloads.
3. In-Memory Databases
These are optimized for microsecond response times and high-throughput workloads.
- Amazon ElastiCache for Redis
- Amazon ElastiCache for Memcached
Use Case: Caching, gaming leaderboards, session storage, and real-time analytics.

4. Time Series Databases
Purpose-built for handling time-stamped or time-series data.
- Amazon Timestream
Use Case: IoT applications, DevOps monitoring, and industrial telemetry data.
5. Graph Databases
Graph databases store relationships between data points, making them ideal for highly connected datasets.
- Amazon Neptune
Use Case: Social networking, recommendation engines, fraud detection, and knowledge graphs.
6. Ledger Databases
Ledger databases provide a transparent, immutable, and cryptographically verifiable transaction log.
- Amazon QLDB (Quantum Ledger Database)
Use Case: Financial transactions, supply chain management, and compliance systems.
7. Data Warehousing
AWS also provides solutions for analyzing large volumes of structured and semi-structured data.
- Amazon Redshift
Use Case: Business intelligence, reporting, and large-scale data analytics.
8. Search Databases
Databases optimized for search and log analytics.
- Amazon OpenSearch Service (successor to Elasticsearch Service)
Use Case: Log analytics, full-text search, application monitoring.
9. Other Specialized Databases
- Amazon Keyspaces (for Apache Cassandra): A managed database service compatible with Cassandra.
- Amazon Neptune Analytics: Advanced analytics for graph databases.

Final Thoughts
So, how many types of databases are in AWS?
AWS provides 15+ purpose-built database services, covering almost every business need — from relational to non-relational, from time-series to ledger, and even specialized services for caching, search, and analytics. The power of AWS databases lies in choosing the right database for the right workload instead of relying on a one-size-fits-all approach.
Get Expert Help with AWS Databases
Managing and choosing the right AWS database service can feel overwhelming, especially if you’re just starting out. That’s where we come in.
Our company provides expert AWS services to help businesses design, migrate, and manage their cloud infrastructure effectively. From AWS RDS to DynamoDB, Redshift, and ElastiCache, we ensure you get the best performance, security, and cost optimization.
Some of the AWS Tools & Services We Work With:
- AWS CloudFormation – Infrastructure as code for database provisioning
- Amazon CloudWatch – Monitoring and logging database performance
- AWS IAM – Secure identity and access management
- AWS Backup – Centralized backup for AWS databases
Whether you need cloud migration, database optimization, or managed services, we can help you get the best out of AWS.

