When to Use RDBMS and When NoSQL? 4 Critical Differences Explained
Databases are the backbone of every modern application, from small business websites to enterprise-grade platforms. But one of the most common questions architects, developers, and even business leaders face is: Should we use a Relational Database (RDBMS) or a NoSQL database?
Relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle have been around for decades. They are proven, reliable, and still power a majority of enterprise systems. On the other hand, NoSQL databases such as MongoDB, Cassandra, and DynamoDB have risen in popularity due to the explosion of unstructured data and the need for massive scalability.
Choosing between the two isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a strategic one. To help you decide, let’s explore the four most critical differences between RDBMS and NoSQL, and when each should be used.
1. Data Model and Structure
The first and most fundamental difference lies in how each system organizes data.
RDBMS is built around structured, tabular data. Think of it as a highly organized spreadsheet where each row represents a record and each column represents an attribute. You must define your schema before inserting data, which makes RDBMS perfect for applications where consistency and relationships are clearly defined—like payroll systems, inventory management, or billing.
NoSQL, by contrast, is schema-less. Instead of rigid tables, you can store data in flexible formats such as JSON documents, key-value pairs, wide-column stores, or even graph structures. This makes NoSQL ideal for applications where data is constantly changing or doesn’t fit neatly into rows and columns. Social media platforms, IoT systems, and recommendation engines all benefit from NoSQL’s flexibility.
2. Scalability
Another critical difference lies in how these databases handle growth.
Traditional RDBMSs scale vertically. If your workload increases, you add more CPU, RAM, or storage to a single machine. This works up to a point but becomes expensive and less practical as data grows into the terabytes and beyond.
NoSQL, on the other hand, was designed with cloud-scale in mind. It scales horizontally—meaning you can simply add more servers to the cluster as your workload increases. This makes it the database of choice for applications expecting rapid user growth or those operating globally, such as e-commerce marketplaces or gaming platforms.
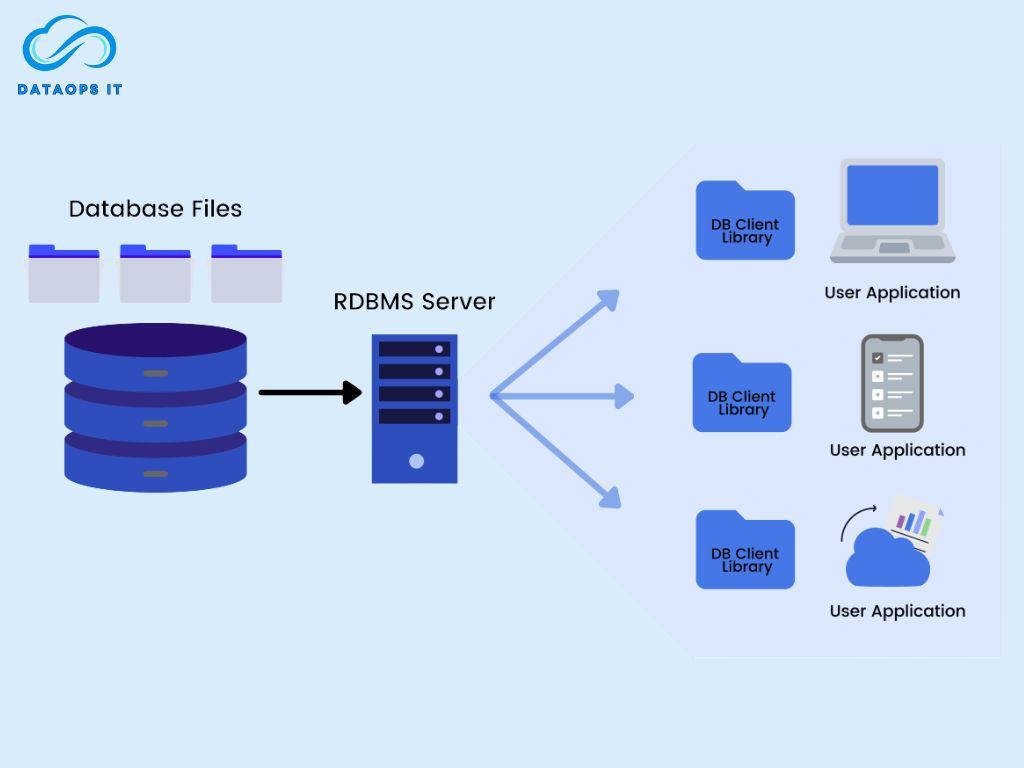
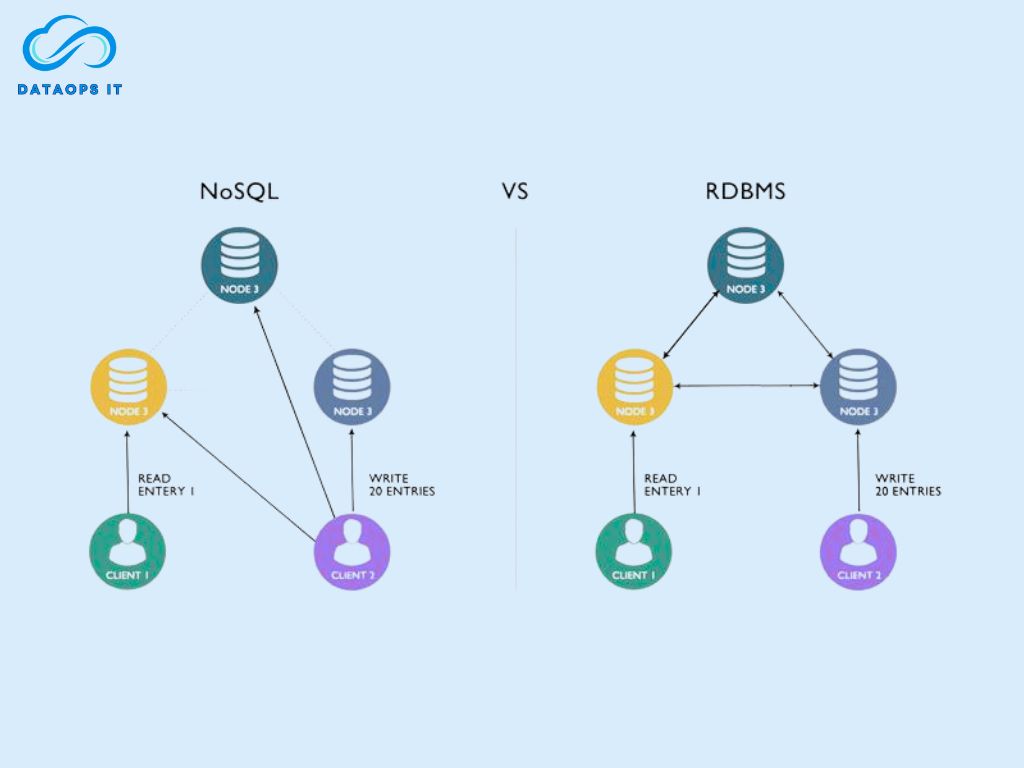
3. Transactions and Consistency
RDBMSs are famous for their ACID compliance: Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. This ensures that transactions are executed with full reliability. If you’re handling money transfers, healthcare records, or airline bookings, this level of transactional integrity is non-negotiable.
NoSQL systems, however, trade strict consistency for speed and availability. Instead of ACID, they typically follow the BASE model: Basically Available, Soft state, Eventual consistency. In other words, your data may take a few moments to synchronize across nodes, but you gain faster response times and resilience. For use cases like chat applications, recommendation engines, or large-scale analytics, this trade-off makes perfect sense.
4. Querying and Performance
The way you query data is also a key difference.
RDBMS uses SQL (Structured Query Language), a powerful, standardized language that makes it easy to perform complex joins, aggregations, and analytics. If your business needs deep reporting or data relationships are at the heart of your application, SQL databases excel.
NoSQL databases, however, don’t use SQL. Each type has its own query method, often optimized for speed in specific scenarios. For example, key-value databases are lightning-fast for lookups, document databases are excellent for flexible JSON queries, and graph databases are unmatched when exploring relationships between nodes—like in social networks or fraud detection.
Conclusion: Which One Should You Choose?
So, when should you choose RDBMS, and when should you go with NoSQL?
The answer depends on your application’s needs. If you require structured data, complex queries, and reliable transactions, RDBMS is the clear winner. If your application demands scalability, flexibility, and the ability to handle unstructured or rapidly changing data, NoSQL is the better fit. In fact, many modern organizations use a hybrid approach, leveraging both depending on the workload.
How AWS Helps You with Databases?
We specialize in helping businesses make the right database decisions using AWS-managed services. With AWS, you don’t need to worry about infrastructure headaches—everything is fully managed, scalable, and secure. Some of the most popular tools include:
- Amazon RDS for managed relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
- Amazon DynamoDB for high-performance, fully managed NoSQL workloads.
- Amazon Aurora, a cloud-optimized relational database that offers up to 5x the performance of standard MySQL.
- Amazon DocumentDB for MongoDB-compatible document storage.
- Amazon Redshift for large-scale analytics and data warehousing.
Whether your application requires the precision of an RDBMS or the flexibility of NoSQL, our AWS-certified team can help you design, migrate, and manage the right solution—so you can focus on growth while AWS handles the complexity.

